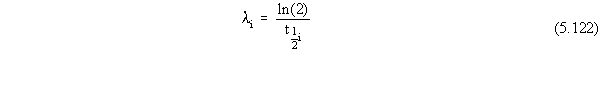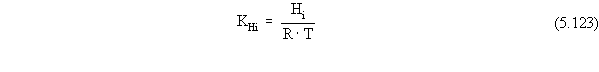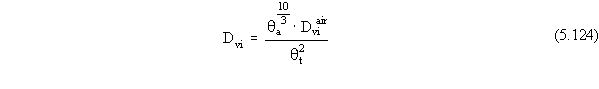5.8 Methods for Calculating Selected Parameters in the Mass Loss Expressions
The first order decay/degradation coefficient
is related to radioactive decay and degradation. The RAAS and MEPAS databases
contain decay half lives for radionuclides and degradation half-lives for
some non-radioactive contaminants. If values of half lives are available,
the decay coefficient is calculated by
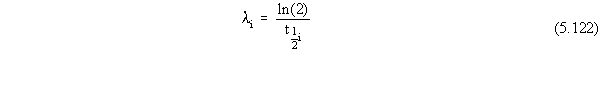
For all volatilization-related calculations, the module uses the modified
Henry’s Law constant (unitless). The Henry’s Law constant is obtained from
the contaminant database and multiplied to obtain the unitless version
by
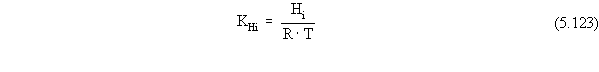
The Darcy water flux density may be entered by the user or calculated
by the module. The user-entered value can be a single value or a piecewise-constant
time series (consisting of an initial value, subsequent values, and the
times at which the flux changes to those subsequent values). The module
will calculate a Darcy water flux density using monthly climatology data
and surface soil data as described in Section 5.1. All the other parameters
in the mass flux equations for the leaching pathway are input directly
by the user.
For wind suspension, a value for the wind suspension soil removal
rate, S, must be obtained. The user may enter a known constant rate, a
known piecewise-constant time series (consisting of an initial value, subsequent
values, and the times at which the flux changes to those subsequent values),
or let the module calculate the rate. If the user does not enter any known
rates, the module will calculate a rate using the methods discussed in
Section 5.2.
For surface water erosion, a value for the water erosion soil
removal rate, E, must be obtained. The user may enter a known constant
rate, a known piecewise-constant time series (consisting of an initial
value, subsequent values, and the times at which the flux changes to those
subsequent values), or let the module calculate the rate. If the user does
not enter any known rates, the module will calculate a sediment removal
rate using the methods discussed in Section 5.3.
The effective vapor diffusion coefficient in soil is given by
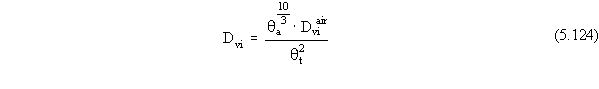
where  is the vapor
diffusion coefficient of contaminant i in air (cm2 yr-1).
is the vapor
diffusion coefficient of contaminant i in air (cm2 yr-1).