5.1.5 Overland Runoff
Overland runoff is computed using the SCS Curve Number
technique (SCS 1972, 1982; Kent 1973; USBR 1977). The factors considered
in this method include surface soil characteristics, vegetative cover,
land use, antecedent moisture conditions, and geographic locale.
To apply this technique in the module, the following is assumed:
- The monthly precipitation depth can be equally distributed among the total
number of recorded precipitation events.
- The number of precipitation events per month can be defined as the mean
number of days with at least 0.254 mm (0.01 in.) of precipitation (as listed
in the LCD).
- There is no overland runoff when the adjusted average monthly temperature
is equal to or below freezing (because precipitation is assumed to be stored
on the land surface in the form of snow).
- The method is applicable, although snow may be covering the land
surface. This condition rarely occurs, because most snow is usually
melted in the first month that the average temperature rises above freezing.
Using the SCS Curve Number technique, the total
monthly runoff from the waste site is estimated as follows:
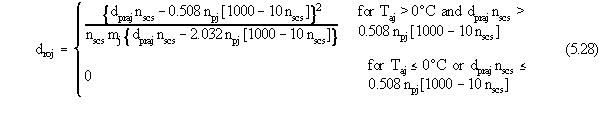
where
droj is the overland runoff for the j-th month (cm)
nscs is the SCS Curve Number used for runoff calculations (unitless)
npj is the number of precipitation events during the j-th month (unitless).
A complete discussion reviewing the development of Equation 5.28 is presented
in Whelan et al. (1987).