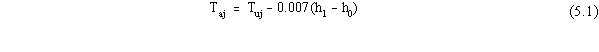5.1.2 Adjusted Average Temperature
Temperatures obtained from the LCD are adjusted for the elevation difference
that may exist between the LCD station and the actual site. In general,
air temperatures decrease about 0.5 to 0.9oC
per 100 m (3 to 5oF per 1000 ft) rise in
altitude (Mockus 1971). Using the ideal gas law with the assumption
of dry adiabatic conditions, Eagleson (1970) derived an approximate lapse
rate (i.e., rate of change of temperature with height in the free atmosphere)
of 1oC decrease per 100 m (5.5oF
decrease per 1000 ft). This dry adiabatic lapse rate is a maximum
rate (excluding superadiabatic conditions). A mean lapse rate as
suggested by Linsley et al. (1975) is a decrease of about 0.7oC
per 100 m (3.8oF per 1000 ft) of vertical
rise. By using the mean lapse rate suggested by Linsley et al. (1975),
the adjusted average monthly temperature is computed as follows:
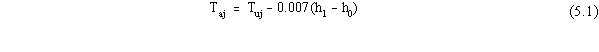
where
Taj is the adjusted average monthly
temperature at the actual site for the j-th month (C)
Tuj is the unadjusted average monthly
temperature at the LCD station for the j-th month ( C)
h0 is the elevation of LCD station (m)
h1 is the elevation of actual site (m).