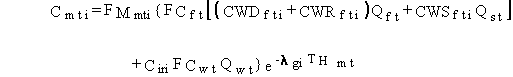2.6 MEAT INGESTION
Animals fed contaminated crops or water can be expected
to produce contaminated meat. The concentration of pollutants in contaminated
feed crops can be generated from the same transport and uptake routes as
for the leafy vegetable and other vegetable exposure pathways. In addition,
for waterborne transport routes, the animals may be fed contaminated water
(groundwater or surface water) from the same source of water as used for
irrigation. For soil contamination animal products may also be contaminated
by animal ingestion of soil. The paths by which pollutants in transport
media may reach animals are shown in Figure 2.2.
For waterborne transport pathways, the exposure evaluation
is performed with the following considerations:
- Transport Medium:
- water concentration at water treatment plant, Cswi or Cgwi, pCi/L or mg/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
-
- loss of pollutants (environmental degradation or radioactive decay) during transport from the pumping station
to the irrigation location
- loss of pollutants during transport in the surface water body by volatilization
- application of irrigation water to animal feed crops and cropland soils
- accumulation of pollutants in soil over the exposure duration
- uptake by roots from soil to edible portions of feed crop plants
- direct deposition onto feed crop plant surfaces and transfer to edible portions of plants
- feeding of crops to animals
- ingestion of soil by animals
- ingestion of irrigation water by animals
- loss of pollutants from animal meat following harvest, prior to consumption by humans.
- Exposure Factors:
- rate of animal meat ingestion and exposure duration.
The application of irrigation water to croplands
results in deposition of pollutants to soils and feed crop plants at a
constant average rate over the period of irrigation. The deposition rate
is given by Equation (18). The soil accumulation factor is also applied
to the analysis, as given by Equations (19) and (20). The concentration
of pollutants in feed-crop plants at the time of feeding to animals is
evaluated as follows for irrigation deposition onto plants:
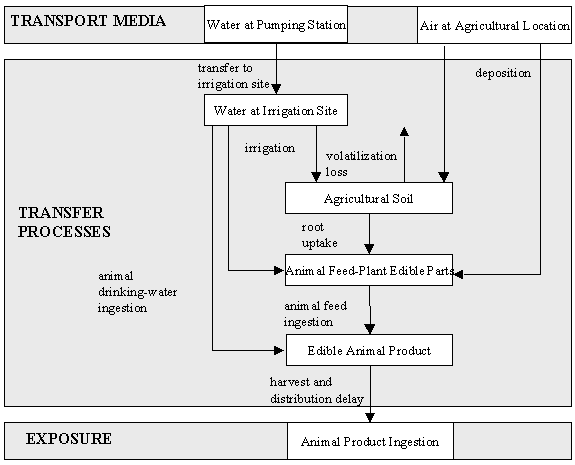
FIGURE 2.2. Pollutant Transfer to Animal Products
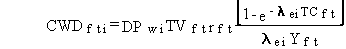
(45)
where
CWDfti = pollutant i concentration in meat animal feed crops at time of feeding from water deposition onto plants (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
DPwi = deposition rate of pollutant i in irrigation water to crops (mg/m2/d or pCi/m2/d)
TVft = translocation factor from plant surfaces to edible parts of the plant for meat animal feed crops (dimensionless)
rft = fraction of deposition retained on edible parts of meat animal feed crops (dimensionless)
lei = ldi + lw
ldi = environmental degradation and decay constant for pollutant i in soil (d-1)
lw = weathering decay constant for losses from plant surfaces (d-1)
TCft = duration of the growing period for meat animal feed crops (d)
Yft = yield of meat animal feed crops (kg/m2).
The plant concentration at the time of harvest for uptake from soil via roots, following irrigation deposition, is estimated as follows:
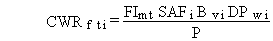
(46)
where
CWRfti = pollutant i concentration in edible parts of meat animal feed crops at time of feeding to animals from root uptake (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
FImt = fraction of year meat animal feed crops are irrigated (dimensionless)
SAFi = soil accumulation factor for the meat ingestion exposure duration for pollutant i (d)
Bvi = soil-to-plant transfer factor for pollutant i (kg dry soil/kg net weight plant)
P = area soil density of farmland (kg dry soil/m2 farmland)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The animals may ingest soil along with the forage
or feed. The soil concentration is evaluated as an average value over the
exposure duration using the same soil accumulation factor as for the plant
root uptake pathway. This factor is evaluated using Equations (19) and
(20). The soil concentration is evaluated as follows:
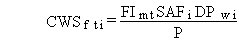
(47)
where CWSfti = average soil concentration for pollutant i eaten by meat animals along with feed (mg/kg dry soil or pCi/kg dry soil)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The concentration of pollutants in meat products
at the time of consumption by humans includes animal intake of feed, water,
and soil, as follows:
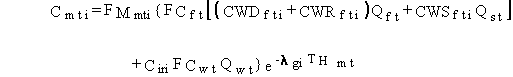
(48)
where
Cmti = concentration of pollutant i in meat at time of consumption by humans (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
FMmti = transfer factor for uptake of pollutant i by animals to meat (d/kg)
FCft = fraction of meat animal feed that is contaminated (dimensionless)
Qft = meat animal ingestion rate of feed (kg/d)
Qst = meat animal intake rate of soil (kg/d)
Ciri = average concentration of pollutant i in irrigation water (mg/L or pCi/L)
FCwt = fraction of meat animal drinking water that is contaminated (dimensionless)
Qwt = meat animal ingestion rate of water (L/d)
lgi = rate constant for decay and loss in confined water system, used to simulate loss during storage and distribution of meat (d-1)
THmt = holdup time between harvest (slaughter) and consumption of animal meat by humans (d)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The average daily dose received by individuals consuming
the contaminated animal meat (for the waterborne transport pathways) is
evaluated as follows for chemical pollutants.
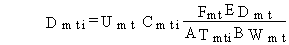
(49)
where
Dmti = average daily dose from ingestion of meat (mg/kg/d)
Umt = ingestion rate of meat by the exposed individual (kg/d)
Fmt = fraction of days per year that meat is eaten (dimensionless)
EDmt = exposure duration for the meat ingestion pathway (yr)
ATmti = averaging time for the meat ingestion pathway for exposure to pollutant i (yr)
BWmt = body weight of individuals exposed by the meat ingestion pathway (kg)
and Cmti is as previously defined. The averaging time for noncarcinogenic chemicals is set to the exposure duration, and the averaging time for carcinogenic chemicals is fixed at 70 years.
For radioactive pollutants, the total lifetime dose
is evaluated as follows:
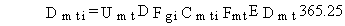
(50)
where
Dmti = total lifetime dose from ingestion of meat (rem)
DFgi = dose conversion factor for ingestion of radionuclide i (rem/pCi) and other terms are as previously defined.
For airborne transport pathways, the exposure evaluation
is performed with the following considerations.
- Transport Medium:
- air at agricultural production location, Cari, pCi/m3 or mg/m3, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
-
- deposition to crops and cropland soils
- uptake by roots from soil to edible portions of plants
- direct deposition onto plant surfaces and transfer to edible portions of plants
- accumulation in soil over the exposure duration
- feeding of crops to animals
- loss of pollutants from animal meat following harvest, prior to consumption by humans
- Exposure factors:
- rate of animal meat ingestion and exposure duration.
The deposition rate from air to plants is given by Equation (26). The
soil accumulation factor, as defined by Equations (19) and (20), is also
applied to this pathway.
The concentration of pollutants in edible parts of
plants from atmospheric deposition is estimated by Equation (45) with parameters
for the air pathway substituted for the irrigation pathway, as follows:
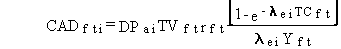
(51)
where
CADfti = pollutant i concentration in feed plants for meat animals at feeding to animal from atmospheric deposition onto plants (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
DPai = deposition rate from air to plants for pollutant i (mg/m2/d or pCi/m2/d)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The meat animal feed plant concentration at the time
of harvest for uptake from soil via roots is estimated as follows:
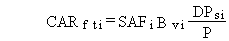
(52)
where
CARfti = pollutant i concentration in edible parts of meat
animal feed plants at feeding to animal from root uptake (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
Bvi = soil-to-plant transfer factor for pollutant i (kg dry
soil/kg wet weight plant)
DPsi = annual average deposition rate of pollutant i to soil
from atmospheric transport and deposition (mg/m2/d or pCi/m2/d)
P = area soil density of farmland (kg dry soil/m2 farmland)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The concentration of pollutants in meat products
at the time of consumption by humans includes animal intake of feed, as
follows:
Cmti = FMmti (CADfti
+ CARfti) FCmt Qft e -
lgiTHmt
(53)
where
Cmti = concentration of pollutant i in meat at time of
consumption by humans (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
FCmt = fraction of meat animal that is contaminated (dimensionless)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The average daily dose received by individuals consuming
the contaminated animal meat (for the atmospheric transport pathway) is
evaluated using Equation (45) for chemical pollutants and by Equation (46)
for radionuclides.
For the measured soil concentration pathway, the
exposure evaluation is performed for an initial soil concentration (measured)
with loss and decay during the exposure period. The following considerations
are included.
- Transport Medium:
- measured soil at the production location, Cmsi,
pCi/kg or mg/kg, expressed as the concentration at the start of the exposure period
- Special Process:
-
- uptake by roots from soil to
- edible portions of animal feed plants
- loss of pollutants from soil by volatilization or decay
- feeding of crops to animals
- ingestion of soil by animals
- loss of pollutants following harvest, prior to consumption of animal products by individuals
- Exposure Factors:
- rate of animal meat ingestion and exposure duration.
The evaluation of feed plant concentration eaten
by meat animals is performed similarly to the evaluation of vegetable plant
concentrations described in the previous sections. The soil average concentration
is evaluated using Equation (32), and the plant concentration is evaluated
using Equation (33). The animal may also ingest soil. The soil concentration
ingested by the meat animal is equal to the average soil concentration
given by Equation (32). The concentration in the animal product is evaluated
as follows:
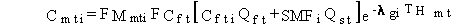
(54)
where Cfti = concentration in meat animal feed for pollutant i (mg/kg wet weight feed or pCi/wet weight feed)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The average daily intake of chemical pollutants is
evaluated using Equation (49) and the lifetime radiation dose for radionuclides
is evaluated using Equation (50).