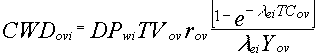Covi = concentration of pollutant i in other vegetables (mg/kg)
l gi = loss and decay rate constant for pollutant i in closed water systems (d-1)
THov = holdup time between harvest of other vegetables and consumption by humans (d)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The average daily dose from ingestion of chemical pollutants (for irrigation water contamination) in other vegetables is evaluated as follows:
(37)
where
Dovi = average daily dose from ingestion of other vegetables (mg/kg/d)
Uov = ingestion rate of other vegetables by the exposed individual (kg/d)
Fov= fraction of days per year that ingestion of other vegetables occurs (dimensionless)
EDov = exposure duration for the other vegetable ingestion pathway (yr)
ATovi = averaging time for other vegetable ingestion pathway for exposure to pollutant i (yr)
BWov = body weight of individuals exposed by other vegetable ingestion pathway (kg). and Covi is as previously defined. The averaging time for noncarcinogenic chemicals is set to the exposure duration, and the averaging time for carcinogenic chemicals is fixed at 70 years.
For radioactive pollutants, the total lifetime dose is evaluated as follows:
(38)
where
Dovi = total lifetime dose from ingestion of other vegetables (rem)
DFgi = dose conversion factor for ingestion of radionuclide i (rem/pCi)
and other terms are as previously defined.
For the atmospheric deposition pathway, the direct deposition of pollutants from air onto edible parts of plants is estimated by Equation (27), with parameters for the air pathway substituted for the irrigation pathway as follows:
(39)
where
CADovi = pollutant i concentration in other vegetables at time of harvest from atmospheric deposition onto plants (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
DPai = deposition rate from air to plants for pollutant i (mg/m2/d or pCi/m2/d)
and other terms are as previously defined.
The soil accumulation factor is also applied to the atmospheric deposition to soil route, as defined by Equations (19) and (20). The plant concentration at the time of harvest for uptake from soil via roots following atmospheric deposition is estimated, as follows:
(40)
where
CARovi = pollutant i concentration in edible parts of other vegetables at harvest from root uptake (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
DPsi = annual average deposition rate of pollutant i to soil from atmospheric transport and deposition (mg/m2/d or pCi/m2/d) and other terms are as previously defined.
The concentration of pollutants in other vegetables at the time of consumption is evaluated as the sum of contributions from the two contamination routes: deposition onto plants and root uptake from soil, as follows:
(41)
where
Covi = concentration of pollutant i in other vegetable crops at the time of consumption (mg/kg or pCi/kg) and other terms are as previously defined.
The average daily dose from ingestion of chemical pollutants (for the atmospheric transport pathway) in other vegetables is evaluated as follows:
(42)
where
Dovi = average daily dose from ingestion of other vegetables (mg/kg/d)
EDov = exposure duration for the other vegetable ingestion pathway (yr)
and other terms are as previously defined. The averaging time for noncarcinogenic chemicals is set to the exposure duration, and the averaging time for carcinogenic chemicals is fixed at 70 years.
For radioactive pollutants, the total lifetime dose is evaluated as follows:
(43)
where Dovi = total lifetime dose from ingestion of other vegetables (rem)
and other terms are as previously defined.
For the measured soil concentration pathway, the exposure evaluation is performed for an initial soil concentration (measured) with loss and decay during the exposure period. The following considerations are included.
- Transport Medium:
- measured soil at the production location, Cmsi,
pCi/kg or mg/kg, expressed as the concentration at the start of the exposure
period
- Special Process:
-
- uptake by roots from soil to
- edible portions of plants
- loss of pollutants from soil by volatilization or decay
- loss of pollutants following harvest, prior to consumption by individuals
- Exposure Factors:
- rate of crop ingestion and exposure duration.
The average concentration is evaluated as the time integral of the activity in the soil divided by the exposure duration, as given by Equation (32).
The concentration in edible parts of plants from root uptake from soil is evaluated as follows:
(44)
where terms are as previously defined.
The average daily intake from ingestion of chemicals in leafy vegetables is evaluated using the plant concentration from Equation (44) and intake Equation (42). For radionuclides, the ingestion dose is evaluated using the plant concentration from Equation (44) and dose Equation (43).