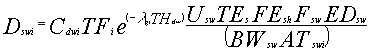2.3 SHOWER WATER INGESTION
While showering with domestic water, individuals may ingest water inadvertently
resulting in a potential for health impacts. This exposure pathway is applicable
to the groundwater and surface water transport pathways. As for the drinking
water pathway, consideration is given to reductions of pollutant concentration
during processing in the water supply treatment plant (if present) and
in transport through the water distribution system to the exposed individuals.
The surface water pathway also includes estimation of losses of volatile
chemicals in transport between the point of entry to the surface water
and the water intake plant.
- Transport Medium:
- water concentration at water treatment plant, Cdwi, pCi/L or mg/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
- removal of pollutants during water treatment loss of pollutants (environmental degradation or radioactive decay) during transport from the treatment plant to the exposure location (households)loss of pollutants during transport in the surface water body by volatilization
- Exposure Factors:
- rate of inadvertent ingestion, frequency of exposure, and exposure duration.
The average daily dose for the inadvertent water ingestion while showering pathway for groundwater transport is evaluated as follows for chemical pollutants:
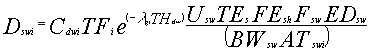
(15)
where
Dswi = average daily ingestion dose for the shower ingestion pathway for pollutant i (mg/kg/d)
Cdwi = concentration of pollutant i in domestic supply water (well or pumping station) used for showering (mg/L or pCi/L)
TFi = water treatment purification factor giving the fraction of pollutant, i, remaining after
treatment (dimensionless)
lgi = loss rate constant for pollutant i in confined water systems (d-1)
THdw = holdup time in transfer of water from the pumping station or well to the consumer (d)
Usw = inadvertent water ingestion rate while showering (L/h)
TEs = length of time period for each shower (h/shower)
FEsh = frequency of showering by the exposed individual (showers/day)
Fsh = fraction of days per year that showering occurs for the inadvertent shower ingestion pathway (dimensionless)
EDsw = exposure duration for the shower water ingestion pathway (yr)
BWsw = body weight of individuals exposed to shower water ingestion pathway (kg)
ATswi = averaging time for the shower water ingestion pathway for exposure to pollutant i (yr).
The averaging time for noncarcinogenic chemicals is set to the exposure
duration, and the averaging time for carcinogenic chemicals is fixed at
70 years.
For radionuclide pollutants the total lifetime dose is evaluated, as
follows, using the dose conversion factor to convert from intake (pCi)
to dose (rem):
Ddwi = Cdwi TFi e (-lgiTHdw)Usw TEs FEsh Fsw DFgi
EDdw 365.25
(16)
where
Ddwi = total lifetime ingestion dose for the shower water ingestion pathway for radionuclide i (rem)
DFgi = dose conversion factor for ingestion of radionuclide i (rem/pCi ingested)
and other terms are as previously defined.
For the surface water transport pathway, the average daily dose is evaluated
as for Equation (15), with the water concentration being corrected for
loss during transport between the entry point to the surface water body
and the pumping station as in Equation (3), as follows:
Cdwi = Cswi (0) e (-lsiTHsw)
(17)
where
Cswi(0) = concentration of pollutant at the pumping station uncorrected for loss during transit in the surface water system (mg/L or pCi/L)
lsi = loss rate constant for pollutant i in surface waters (d-1)
Tsw = transit time in the surface water system between the point of entry and the pumping station (d).