2.24 AIR EXTERNAL RADIATION
While radioactive pollutants are being transported
past individuals, radiation emitted from the plume may cause radiation
exposure. This pathway will normally be overshadowed by the inhalation
route except when noble gas radionuclides are involved. The exposure for
this pathway is estimated using dose conversion factors for material uniformly
distributed in air. The considerations given to this exposure pathway are
as follows.
- Transport Medium:
- air concentration at selected locations in the region about the release site, Cari, pCi/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
- none (the transport component accounts for special processes during downwind transport)
- Exposure Factors:
- exposure rate and exposure duration.
The air concentration is used to estimate the total
lifetime dose for the air external exposure pathway for atmospheric transport
for radionuclides as follows:
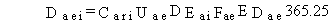
(110)
where
Daei = total lifetime dose for the air external exposure pathway (rem)
Cari = concentration of pollutant i in air at the point of exposure (pCi/m3)
Uae = exposure rate (h/d)
DEai = dose conversion factor for external exposure to airborne radionuclide i (rem/h per pCi/m3)
Fae = fraction of days per year external exposure to air occurs (dimensionless)
EDae = exposure duration for the air external exposure pathway (yr).