2.20 SWIMMING EXTERNAL RADIATION
Individuals swimming in water contaminated with radioactive
pollutants may receive external radiation exposure. This exposure pathway
is applicable to the surface water transport pathway when aquatic recreational
activities are specified. As for the drinking water pathway, consideration
is given to losses of volatile chemicals in transport between the point
of entry to the surface water and the water intake plant.
- Transport Medium:
- radionuclide concentration in water at the surface water body location for aquatic recreational activities, Cswi, pCi/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
- loss of pollutants during transport in the surface water body by volatilization immersion of the swimmer in water
- Exposure Factors:
- frequency of swimming exposure and exposure duration.
The total lifetime dose from external exposures to radionuclides while swimming is evaluated as follows:
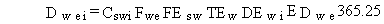
(105)
where
Dwei = total lifetime dose for radionuclide pollutant i from swimming in contaminated surface water (rem)
Cswi = concentration of radionuclide i in surface water at the swimming location (pCi/L)
Fwe = fraction of days per year that swimming occurs (dimensionless)
FEsw = average frequency of swimming events (events/d)
TEw = duration of an average swimming event (h/event)
DEwi = dose conversion factor for immersion in contaminated water for radionuclide i (rem/h per pCi/L)
EDwe = exposure duration for the swimming pathway (yr) and the final term is as previously defined.