2.2 SHOWER WATER DERMAL CONTACT
Use
of domestic water for showering will expose individuals to pollutants from
dermal contact with water. Pollutants will be taken into the body through
the skin and provide a potential for health impacts. This exposure pathway
is applicable to the groundwater and surface water transport pathways.
As for the drinking water pathway, consideration is given to reductions
of pollutant concentrations during processing in the water supply treatment
plant (if present) and in transport through the water distribution system
to the exposed individuals. The surface water pathway also includes estimation
of losses of volatile chemicals in transport between the point of entry
to the surface water and the water intake plant.
- Transport Medium:
- water concentration at the domestic water treatment plant, Cdwi, pCi/L or mg/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
- removal of pollutants during water treatment loss of pollutants (environmental degradation or radioactive decay) during transport from the treatment plant to the exposure location (households) loss of pollutants during transport in the surface water body by volatilization absorption through the skin during showering event
- Exposure Factors:
- area of skin exposed, frequency of exposure, and exposure duration.
Dermal exposures
to chemicals are treated as ingestion intakes with correction for the fraction
of the chemical absorbed in passing through the GI tract. The correction
is not needed for dermal exposures to radionuclides because dose factors
are available in MEPAS for radionuclide intake through the skin. The intake
from dermal contact with water is evaluated using a model that first estimates
the dermal intake per event (shower). This value is then used with shower
frequency data and exposure parameters to determine the average daily dose.
The
intake per shower is evaluated using methods suggested by USEPA (USEPA
1992), as described in the following discussion.
For
inorganic chemicals and radionuclides, the intake per shower per unit area
of skin contacted is evaluated as follows:
Ishi = 10-3 Cdwi TFi e(-lgiTHdw) Kpi TEs
(4)
where
Ishi = amount of pollutant i absorbed through the skin during one shower event per unit area of skin contacted (mg/cm2/shower or pCi/cm2/shower)
10-3 = units conversion factor (L/cm3)
Cdwi = concentration of pollutant i in domestic water used for shower-ing (mg/L or pCi/L)
TFi = water treatment purification factor giving the fraction of pollutant, i, remaining after treatment (dimensionless)
lgi = loss rate constant for pollutant i in confined water systems (d-1)
THdw = Holdup time in transfer of water from the pumping station or well to the consumer (d)
Kpi = skin absorption permeability constant for pollutant i (cm/h)
TEs = duration of one shower (h).
For
organic chemicals, the USEPA model uses the permeability constant for the
pollutant of interest, the skin thickness, and the duration of one shower
event to estimate the total amount of pollutant transferred through the
skin. These parameters are used in a six-step procedure (as defined
in USEPA 1992a) to esti-mate the absorbed dose per unit area per event,
as follows:
Step 1 - Evaluate the permeability constant. This value is supplied in MEPAS from the chemical database or estimated from the octanol-water par-ti-tion coefficient, Kowi.
Step 2 - Calculate B (dimensionless), given by
Step 3 - Determine the diffusion coefficient for skin, DSi (cm2/h), given by
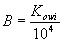
(5)
DSi = 0.001906 1sc 10-0.0061 MWi
(6)
where MWi = molecular weight of the organic compound i and the skin (stratum corneum) thickness, lsc, set to 10-3 cm.
Step 4 - Calculate the delay time, T (h) from the following equation:
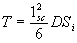
(7)
where terms are as previously defined.
Step 5 - Calculate the time to reach steady state, t* (h) from the following procedure dependent on the value calculated for B.
For B 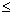 0.1, then t* = 2.4 t
0.1, then t* = 2.4 t
For 0.1 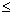 B
B 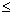 1.17,
then t* = (8.4 + 6 log B) t
1.17,
then t* = (8.4 + 6 log B) t
For B 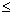 1.17, then
1.17, then
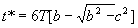
(8)
where the constants b and c are given, as follows:
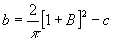
(9)
and
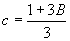
(10)
where terms are as previously defined.
Step 6 - Calculate the amount absorbed per event per unit area, Ishi, using the following equations
depending on the value calculated for t* relative to the event duration, TEs.
For TEs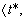
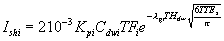
(11)
and for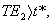
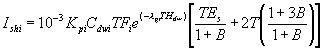
(12)
where 10-3 is a unit conversion factor (L/cm3) and other terms are as previously defined.
The average daily dose, corrected
by the gastrointestinal tract absorption fraction, is given as follows:
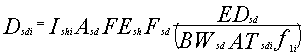 (13)
(13)
where
Dsdi = average daily dose from chemical pollutant i via dermal absorption from water contact while showering, equivalent to oral intake (mg/kg/d)
Ishi = dose absorbed per unit area per shower for pollutant i (mg/cm2-shower)
Asd = area of skin exposed to contaminated water while showering (cm2)
FEsh = frequency of showers (showers/day)
Fsd = fraction of days per year that showering occurs (dimensionless)
EDsd = exposure duration for dermal absorption while showering pathway (yr)
BWsd = body weight of exposed individual for dermal absorption while showering pathway (kg)
ATsdi = averaging time for dermal absorption while showering pathway for pollutant i (yr)
f1i = fraction of pollutant i absorbed in passing through the GI tract following ingestion (dimensionless).
The
average daily dose as computed by Equation (13) is equivalent to oral exposure
because the GI absorption correction has been applied. The averaging time
for noncarcinogenic chemicals is set to the exposure duration, and the
averaging time for carcinogenic chemicals is fixed at 70 years. The equation
is used for all pollutants except radionuclides.
For radionuclides,
the GI absorption fraction and body weight are not applied because radionuclide
specific dose conversion factors for dermal intake are provided in the
chemical database for the 70-kg reference man. The dermal dose factors
were calculated using the CINDY software package (Strenge et al. 1992;
Kennedy and Strenge 1992). The equation for radionuclides is as follows:
Dsdi = Ishi Asd FEsh Fsd
DFdi EDsd 365.25
(14)
where
Dsdi = total lifetime dose via dermal absorption for radionuclide i (rem)
DFdi = dose conversion factor for dermal absorption of radionuclide i (rem/pCi)
and other terms are as previously
defined.
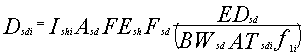 (13)
(13)