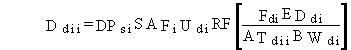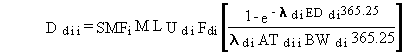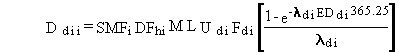2.19 INHALATION OF RESUSPENDED SOIL
The atmospheric transport pathway and the measured
soil pathways involve material contained in soil. This material may be
suspended and inhaled by nearby individuals resulting in inhalation exposure.
The atmospheric transport component provides estimates of soil deposition
from which the concentration in soil over the exposure period may be estimated.
The soil concentration is used as the starting point in the resuspension
model to estimate the air concentration to which individuals are exposed.
- Transport Medium:
- soil concentration at the location of the exposed individual, Casi, pCi/m2 or mg/m2, expressed as an annual deposition accumulation value
- Special Process:
- accumulation of pollutants in soil over the exposure duration for the soil ingestion pathway resuspension of pollutants in soil to air
- Exposure Factors:
- ingestion rate of soil, event frequency, and exposure duration.
The soil concentration is provided from the atmospheric
transport analysis as an average annual deposition amount averaged over
a 70-year exposure period. The accumulation of pollutants in soil over
a multiple-year exposure duration is estimated using the deposition and
accumulation Equations (19) and (20). The concentration in the air above
the contaminated soil is estimated by using the resuspension factor method.
This method relates the air concentration to soil concentration by a single
factor to represent the average ratio of air concentration to soil concentration.
The average daily dose for chemical pollutants from
inhalation of resuspended pollutants following atmospheric transport and
deposition is evaluated as follows:
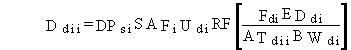
(101)
where
Ddii = average daily dose for chemical pollutant i from inhalation of resuspended pollutants (mg/kg/d)
DPsi = annual average deposition rate pollutant i to soilfrom atmospheric transport and deposition (mg/m2/d)
SAFi = soil deposition and accumulation factor for the soil pathways evaluated for the current exposure duration (d)
Udi = inhalation rate of air for the resuspension pathway (m3/d)
RF = resuspension factor (m-1)
Fdi = fraction of days per year that resuspension inhalation exposure occurs (dimensionless)
EDdi = exposure duration for the pollutant resuspension pathway (yr)
ATdii = averaging time for pollutant i for the pollutant resuspension pathway (yr)
BWdi = body weight of exposed individual for the pollutant resuspension pathway (kg).
For radionuclide pollutants, the total lifetime dose is evaluated as follows:
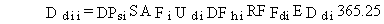
(102)
where
Ddii = total lifetime dose for radionuclide pollutant i from inhalation of resuspended pollutants (rem)
DPsi = annual average deposition rate of radionuclide i to soil from atmospheric transport and deposition (pCi/m2/d)
DFhi = dose conversion factor for inhalation of radionuclide i (rem/pCi ingested) and other terms are as previously defined.
When the measured soil pathway is used, the soil
concentration is expressed per unit mass of soil (rather than per unit
area as for the atmospheric transport pathway). The air concentration is
evaluated for the measured soil pathway using a mass loading factor that
provides the amount of soil airborne. This airborne soil is assumed to
have the same pollutant concentration as the measured soil.
- Transport Medium:
- measured soil concentration at selected locations, Cmsi, pCi/kg or mg/kg, expressed as the amount present at the start of the first 70-year period
- Special Process:
- loss of pollutant from the soil according to the defined soil retention half time suspension of soil containing the pollutants
- Exposure Factors:
- inhalation rate and exposure duration.
The soil average concentration is evaluated using
Equation (32) and is used to estimate the average daily dose for inhalation
of suspended pollutants as follows:
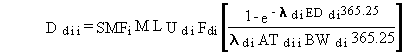
(103)
where
Ddii = average daily dose for chemical pollutant i from inhalation of suspended pollutants for the measured soil pathway (mg/kg/d)
SMFi = average soil concentration of pollutant i (mg/kg)
ML = mass loading factor for airborne particulate material (kg/m3)
Udi = inhalation rate of air for the resuspension pathway (m3/d)
Fdi = fraction of days in a year that exposure to suspended material occurs (dimensionless)
EDdi = exposure duration for the pollutant resuspension pathway (yr)
ATdii = averaging time for pollutant i for the pollutant resuspension pathway (yr)
BWdi = body weight of exposed individual for the pollutant resuspension pathway (kg)
ldi = environmental loss rate constant for pollutant i in soil (d-1)
365.25 = units conversion factor (d/yr).
For radionuclide pollutants, the total lifetime dose is evaluated
as follows:
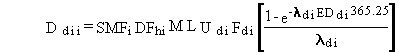
(104)
where
Ddii = total lifetime dose for radionuclide i from inhalation of suspended pollutants for the measured soil pathway (rem)
SMFi = average soil concentration over the exposure period for radionuclide pollutant i (pCi/kg)
and other terms are as previously defined.