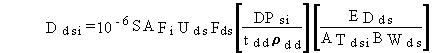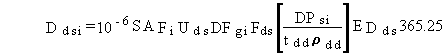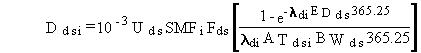2.14 SOIL INGESTION
During normal daily activities, individuals ingest
small amounts of soil from such sources as outdoor soil and indoor house
dust (derived from outdoor soil). In MEPAS, there are two situations in
which soil ingestion is evaluated: deposition following atmospheric transport
and cases for which measured soil concentrations are available. The shoreline
sediment ingestion pathway is treated separately from the soil ingestion
pathway.
The considerations given to estimation of the soil
ingestion dose from atmospheric transport and deposition are as follows.
- Transport Medium:
- soil concentration at the location of the exposed individual, Casi, pCi/m2 or mg/m2, expressed as an annual deposition accumulation value
- Special Process:
- accumulation of pollutants in soil over the exposure duration for the soil ingestion pathway
- Exposure Factors:
- ingestion rate of soil, event frequency, and exposure duration.
The soil concentration is provided from the transport
analysis as an average annual deposition amount, averaged over a 70-year
exposure period. The accumulation of pollutants in soil over a multiple-year
exposure duration is estimated using the deposition and accumulation Equations
(19) and (20) given in Subsection 2.4. The average daily dose for chemical
pollutants from soil ingestion is evaluated as follows for the atmospheric
transport and deposition pathway:
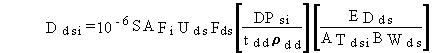
(81)
where
Ddsi = average daily dose for chemical pollutant i from ingestion of soil (mg/kg/d)
10-6 = units conversion factor (m3/cm3)
SAFi = soil deposition and accumulation factor for the soil ingestion pathway exposure duration (d)
Uds = ingestion rate for soil (g/d)
Fds = fraction of days per year that soil ingestion occurs (dimensionless)
DPsi = annual average deposition rate to soil for pollutant i (mg/m2/d)
tdd = thickness of soil layer that deposited pollutant is uniformly distributed within (m)
rdd = density of soil deposited pollutant is distributed within (g/cm3)
EDds = exposure duration for the soil ingestion pathway (yr)
ATdsi = averaging time for pollutant i for the soil ingestion pathway (yr)
BWds = body weight of exposed individual for the soil ingestion pathway (kg).
For radionuclide pollutants, the total lifetime dose is evaluated as follows:
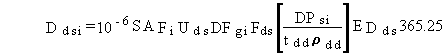
(82)
where
Ddsi = total lifetime dose for radionuclide pollutant i from ingestion of soil (rem)
DFgi = dose conversion factor for ingestion of radionuclide i (rem/pCi ingested)
DPsi = annual average deposition rate of pollutant i to soil from atmospheric transport and deposition (pCi/m2/d) and other terms are as previously defined.
When measured soil concentrations are defined by
the user, the exposed individuals are assumed to ingest the soil directly
without special processes being applied to the concentrations provided,
except for losses according to the environmental half time for soil and
radioactive decay. The average soil concentration during the exposure period
is evaluated using Equation (32). The average daily dose from inadvertent
soil ingestion for the measured soil pathway is evaluated as follows for
chemical pollutants:
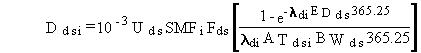
(83)
where
Ddsi = average daily dose for chemical pollutant i from ingestion of soil (mg/kg/d)
Uds = ingestion rate for soil (g/d)
10-3 = units conversion factor (kg/g)
SMFi = average soil concentration for pollutant i (mg/kg)
Fds = fraction of days per year that soil ingestion occurs (dimensionless)
ldi = environmental loss rate constant for surface soil for pollutant i (d-1)
EDds = exposure duration for the soil ingestion pathway (yr)
ATdsi = averaging time for pollutant i for the soil ingestion pathway (yr)
BWds = body weight of exposed individual for the soil ingestion pathway (kg).
For radionuclide pollutants, the total lifetime dose is evaluated as follows:
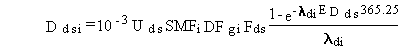
(84)
where
dsi = total lifetime dose for radionuclide pollutant i from ingestion of soil (rem)
SMFi = average soil concentration for pollutant i (pCi/kg) and other terms are as previously defined.