2.13 SHORELINE SEDIMENT INGESTION
Individuals may inadvertently ingest sediments while
involved in shoreline recreational activities. This pathway is based on
the shoreline sediment concentration, as defined in Subsection 2.12, and
is similar to the soil ingestion pathway (described in Subsection 2.14).
For the shoreline sediment ingestion pathway, the following considerations
are given to the exposure evaluation.
- Transport Medium:
- surface water concentration in the water at the shoreline location, Cswi, pCi/L or mg/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
- loss of pollutants during transport in the surface water body by volatilization transfer of pollutant from water to shoreline sediment accumulation of pollutant in sediment over time contact of individuals with shoreline sediment
- Exposure Factors:
- ingestion rate of sediments, shoreline event frequency, and exposure duration.
The loss of pollutants during transport in the surface
water body is evaluated using Equation (3). The transfer and accumulation
of pollutants in sediments is estimated using the same model described
in Subsection 2.12. The concentration to which individuals are exposed
is evaluated using Equations (68) and (69). This concentration is used
to estimate the average daily dose to chemical pollutants as follows:

(79)
where
Dhsi = average daily dose for chemical pollutant i from ingestion of shoreline sediment (mg/kg/d)
10-3 = units conversion factor (kg/g)
Cssi = shoreline sediment concentration for pollutant i at the location of recreational shoreline use (mg/kg or pCi/kg)
FEsl = shoreline use event frequency (events/d)
TEl = length of each shoreline exposure event (h/event)
Uhs = ingestion rate for shoreline sediment (g/h)
Fhs = fraction of days per year that shoreline sediment ingestion occurs (dimensionless)
EDhs = exposure duration for the shoreline sediment ingestion pathway (yr)
AThsi = averaging time for pollutant i for the shoreline sediment ingestion pathway (yr)
BWhs = body weight of exposed individual for the shoreline sediment ingestion pathway (kg).
The total lifetime dose to radionuclide pollutants from
inadvertent ingestion of shoreline sediments is estimated as follows:
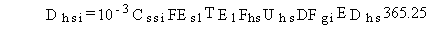
(80)
where
Dhsi = total lifetime dose for radionuclide pollutant i from ingestion of shoreline sediment (rem)
DFgi = dose conversion factor for ingestion of radionuclide i (rem/pCi ingested) and other terms are as previously defined.