2.10 SWIMMING WATER INGESTION
Individuals may inadvertently ingest small amounts
of water while swimming. The following considerations are given to estimating
the inadvertent water ingestion exposure to surface water while swimming.
- Transport Medium:
- surface water concentration in the water body used for swimming, Cswi, pCi/L or mg/L, expressed as a 70-year average value
- Special Process:
- loss of pollutants during transport in the surface water body by volatilization
- Exposure Factors:
- swimming frequency, time, and inadvertent ingestion rate.
The loss of pollutants during transport in the surface
water body is evaluated using Equation (3). The swimming frequency and
time period of each swimming event determine the average time spent swimming
per day. The average daily dose for chemical pollutants from the swimming
water ingestion exposure pathway is evaluated as follows:
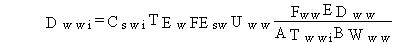
(70)
where
Dwwi = average daily dose from pollutant i from inadvertent ingestion of water while swimming (mg/kg/d)
Cswi = surface water concentration of pollutant i at the location of swimming (mg/L)
TEw = duration of an average swimming event (hours/event)
FEsw = average frequency of swimming events (events/d)
Uww = rate of inadvertent ingestion of water while swimming (L/h).
Fww = fraction of days per year that swimming occurs (dimensionless)
EDww = exposure duration for the swimming water ingestion pathway (yr)
ATwwi = averaging time for the swimming water ingestion pathway for exposure to pollutant i (yr)
BWww = body weight of individuals exposed by the swimming water ingestion pathway (kg).
The fraction of days per year that swimming occurs (Fww)
will normally be set to a value of 1.0, with the average frequency of swimming
events (FEsw) set to represent the times a person swims per
year. For example, if swimming occurs 7 times per year, the average frequency
of swimming events is 7/365, and the fraction of days per year that swimming
activities could occur is 1.0 (all year). If the scenario is to represent
just the summer months (such as for a transient recreational population),
then the fraction of days per year could be set to 0.25 (one quarter of
a year). Use of the two parameters must be coordinated. Because both parameters
are used as multiplicative factors, either parameter can be used to represent
the exposure situation. The averaging time for noncarcinogenic chemicals
is set to the exposure duration, and the averaging time for carcinogenic
chemicals is fixed at 70 years. The total lifetime dose for radionuclide
pollutants from the swimming water ingestion exposure pathway is evaluated
as follows:
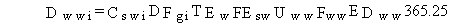
(71)
where
Dwwi = total lifetime dose from radionuclide pollutant i from inadvertent ingestion of water while swimming (rem)
Cswi = surface water concentration of pollutant i at the location
DFgi = dose conversion factor for ingestion of radionuclide i (rem/pCi ingested)
and other terms are as previously defined.