GENII 2.0 Atmospheric Transport Chronic Gaussian Plume Model
Gaussian Plume - Most commonly used atmospheric dispersion model. It is consistent with the random nature of turbulence. It is a solution to the Fickian (K-theory) diffusion equation for constants K and u.
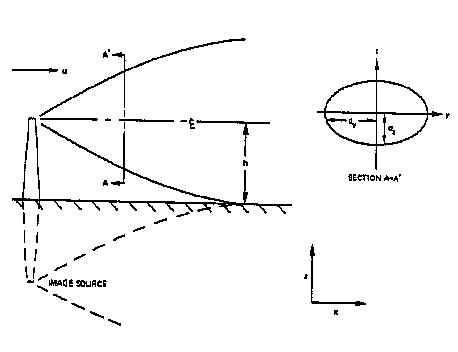
Chronic Plume Model:
Straight-line sector-averaged Gaussian
Runs on hourly observations or joint-frequency data
Multiple independent sources
Ground-level or elevated releases
Point or area sources
Finite flow correction
Sectors by 16 compass points or 10 degrees
Radial or square output grid
Parameterizations Available in All Air Models
Building wake/low-speed meander
Buoyancy-induced diffusion
Plume rise/downwash corrections:
Diabatic wind profile
Sources of Data for Atmospheric Models:
Hourly data
CD-144 format (National Climatic Data Center, NCDC)
SAMSON format (NCDC)
1st order stations 161-1990 on 3 CDs
Precipitation in TD-3240 format (NCDC)
Joint-frequency data
- STAR (ISC-3)
- GENII V.1.485
Limitations:
Up to 100 radionuclides may be considered in one case
Decay chains are limited to 9 members (be careful not to use the MEPAS RMDLIB.DAT)
The radon-diffusion model is not yet implemented in the near-field model
The software is still in testing - please report problems!




 FRAMES Tutorial Home | Security & Privacy | Contact Us
FRAMES Tutorial Home | Security & Privacy | Contact Us